What is hashing? Hashing is the process of transforming any given key or a string of characters into another value. This is usually represented by a shorter, fixed-length value or key that represents and makes it easier to find or employ the original string.
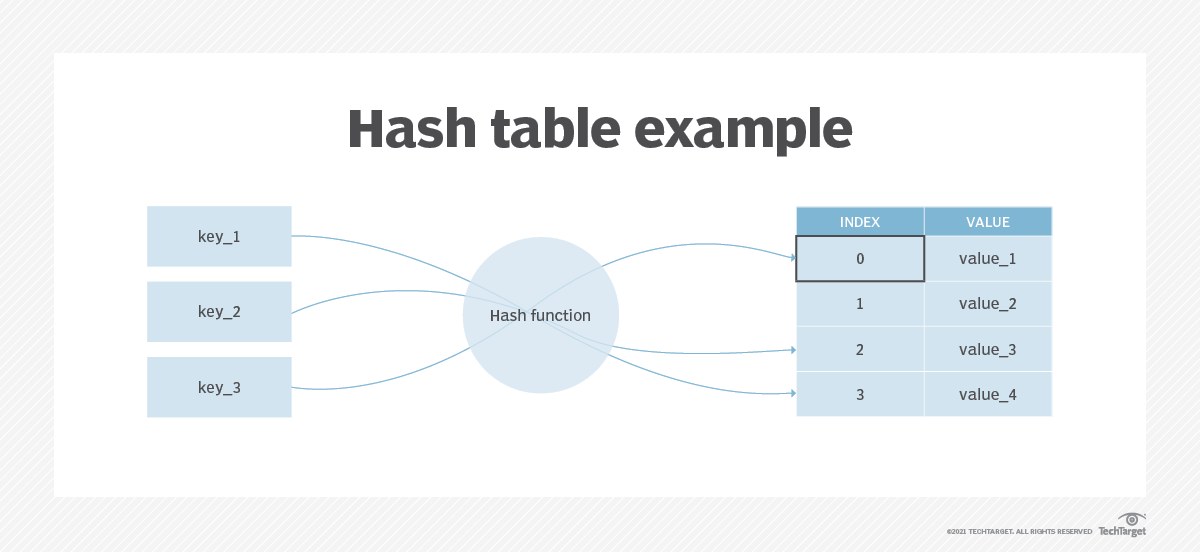
The most popular use for hashing is the implementation of hash tables. A hash table stores key and value pairs in a list that is accessible through its index. Because key and value pairs are unlimited, the hash function will map the keys to the table size. A hash value then becomes the index for a specific element.
A hash function generates new values according to a mathematical hashing algorithm, known as a hash value or simply a hash. To prevent the conversion of hash back into the original key, a good hash always uses a one-way hashing algorithm.
Hashing is relevant to – but not limited to – data indexing and retrieval, digital signatures, cybersecurity and cryptography.
What is hashing used for? Data retrieval Hashing uses functions or algorithms to map object data to a representative integer value. A hash can then be used to narrow down searches when locating these items on that object data map.
For example, in hash tables, developers store data – perhaps a customer record – in the form of key and value pairs. The key helps identify the data and operates as an input to the hashing function, while the hash code or the integer is then mapped to a fixed size.
Hash tables support functions that include the following:
insert (key, value) get (key) delete (key)
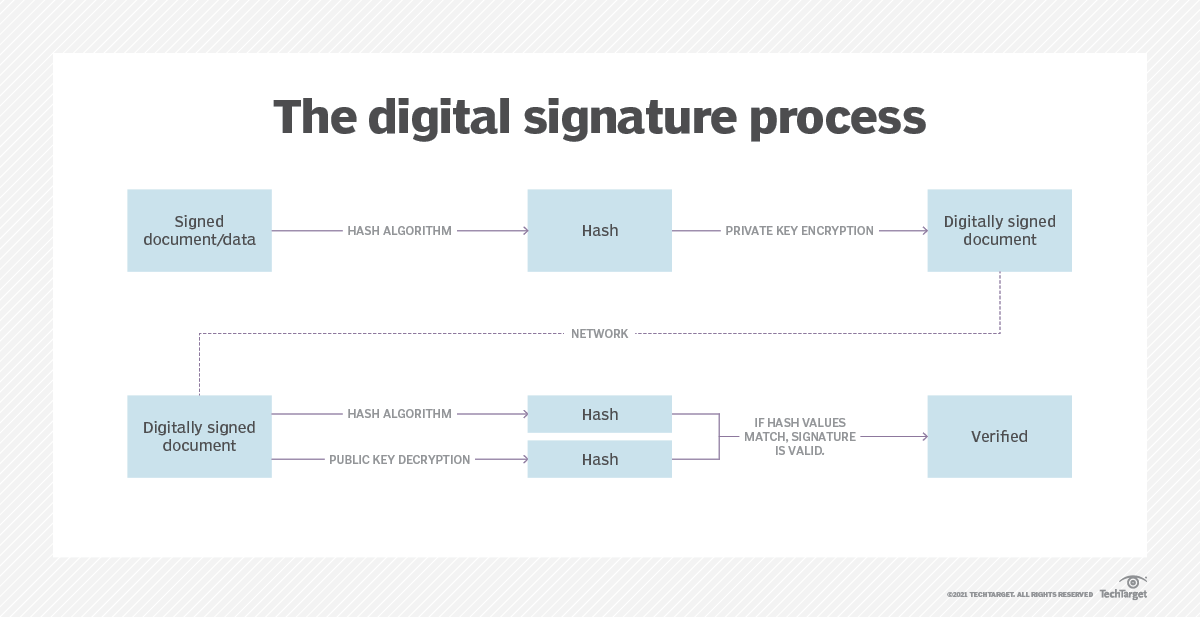
Digital signatures In addition to enabling rapid data retrieval, hashing helps encrypt and decrypt digital signatures used to authenticate message senders and receivers. In this scenario, a hash function transforms the digital signature before both the hashed value (known as a message digest) and the signature are sent in separate transmissions to the receiver.
Upon receipt, the same hash function derives the message digest from the signature, which is then compared with the transmitted message digest to ensure both are the same. In a one-way hashing operation, the hash function indexes the original value or key and enables access to data associated with a specific value or key that is retrieved.
Hashing คืออะไร
Hashing เป็นการเอา data ที่ไม่ว่าจะมีความยาวแค่ไหนก็ตาม (variable length input) (เช่น ungkana, 12 July 2021) มาผ่าน formula (algorithm) และได้ผลออกมาเป็น hash value (หรือ message digest) ซึ่งจะมีความยาวเท่าเดิมเสมอ (Fixed Length Output) ขึ้นอยู่กับ formula ที่เราใช้ (เช่น AES, ECC, MD5 เป็นต้น)
ในที่นี้ ถ้า input data มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงแม้แต่นิดเดียว hash value output จะเปลี่ยนแปลงไปทันที
ตัวอย่างเช่น
Hashing เป็น one-way function กล่าวคือ เราไม่สามารถเอาค่า hash มาแปลงเป็น original data ได้โดยตรง แต่หากเราต้องการที่จะรู้ว่า orinal data คืออะไร ไม่สามารถ run ผ่าน formula เพื่อแปลงค่ากลับไปเป็นค่าเดิมได้ เราจะต้องเอา hash value ไป map กับ orignal data และค่า hash ของแต่ละตัว เพื่อระบุว่า original data คืออะไร นั่นเอง
หากเราต้องการทำเป็นแบบ 2 ways นั่นคือ เรามีความตั้งใจที่จะแปลง data กลับไปเป็นค่าตั้งต้น เราอาจจะต้องพิจารณาการทำ encrypting แทน hashing ซึ่ง encrypted data สามารถ run ผ่าน decryption formula เพื่อกลับไปยังค่าเริ่มต้นได้
