What is penetration testing? Penetration testing (or pen testing) is a security exercise where a cyber-security expert attempts to find and exploit vulnerabilities in a computer system. The purpose of this simulated attack is to identify any weak spots in a system’s defenses which attackers could take advantage of.
This is like a bank hiring someone to dress as a burglar and try to break into their building and gain access to the vault. If the ‘burglar’ succeeds and gets into the bank or the vault, the bank will gain valuable information on how they need to tighten their security measures.
Who performs pen tests? It’s best to have a pen test performed by someone with little-to-no prior knowledge of how the system is secured because they may be able to expose blind spots missed by the developers who built the system. For this reason, outside contractors are usually brought in to perform the tests. These contractors are often referred to as ‘ethical hackers’ since they are being hired to hack into a system with permission and for the purpose of increasing security.
Many ethical hackers are experienced developers with advanced degrees and a certification for pen testing. On the other hand, some of the best ethical hackers are self-taught. In fact, some are reformed criminal hackers who now use their expertise to help fix security flaws rather than exploit them. The best candidate to carry out a pen test can vary greatly depending on the target company and what type of pen test they want to initiate.
What are the types of pen tests? Open-box pen test - In an open-box test, the hacker will be provided with some information ahead of time regarding the target company’s security info. Closed-box pen test - Also known as a ‘single-blind’ test, this is one where the hacker is given no background information besides the name of the target company. Covert pen test - Also known as a ‘double-blind’ pen test, this is a situation where almost no one in the company is aware that the pen test is happening, including the IT and security professionals who will be responding to the attack. For covert tests, it is especially important for the hacker to have the scope and other details of the test in writing beforehand to avoid any problems with law enforcement. External pen test - In an external test, the ethical hacker goes up against the company’s external-facing technology, such as their website and external network servers. In some cases, the hacker may not even be allowed to enter the company’s building. This can mean conducting the attack from a remote location or carrying out the test from a truck or van parked nearby. Internal pen test - In an internal test, the ethical hacker performs the test from the company’s internal network. This kind of test is useful in determining how much damage a disgruntled employee can cause from behind the company’s firewall. How is a typical pen test carried out? Pen tests start with a phase of reconnaissance, during which an ethical hacker spends time gathering data and information that they will use to plan their simulated attack. After that, the focus becomes gaining and maintaining access to the target system, which requires a broad set of tools.
Tools for attack include software designed to produce brute-force attacks or SQL injections. There is also hardware specifically designed for pen testing, such as small inconspicuous boxes that can be plugged into a computer on the network to provide the hacker with remote access to that network. In addition, an ethical hacker may use social engineering techniques to find vulnerabilities. For example, sending phishing emails to company employees, or even disguising themselves as delivery people to gain physical access to the building.
The hacker wraps up the test by covering their tracks; this means removing any embedded hardware and doing everything else they can to avoid detection and leave the target system exactly how they found it.
What happens in the aftermath of a pen test? After completing a pen test, the ethical hacker will share their findings with the target company’s security team. This information can then be used to implement security upgrades to plug up any vulnerabilities discovered during the test. These upgrades can include rate limiting, new WAF rules, and DDoS mitigation, as well as tighter form validations and sanitization. การตรวจสอบจุดอ่อน หรือ ช่องโหว่ของ Application ที่มีใช้งานในองค์กรนับเป็นมาตรการในการรับมือภัยคุกคามทางไซเบอร์อย่างหนึ่ง ในโลก IT มีการพัฒนาอย่างรวดเร็วทั้งในด้านของเทคโนโลยี ระบบรักษาความปลอดภัย ระบบการช่องทางการสื่อสาร และแน่นอนภัยคุกคามต่างๆ ก็เช่นเดียวกันที่มีการปรับตัวเพื่อให้สามารถหลบหลีกการตรวจจับ หรือ Security Control ต่างๆ
แนวทางในการวางระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยเป็นสิ่งที่จำเป็นอย่างยิ่ง หลายองค์กรมีการวางมาตรการเหล่านี้ไว้เป็นอย่างดี ไม่ว่าจะเป็นหลักการออกแบบในลักษณะ Defense in Depth, แนวคิดด้าน Think for the Worst Case ต่างๆ นาๆ ทั้งนี้ก็เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ที่ออกมามีความสมดุลย์กันที่สุดระหว่าง Security, Functionality, Friendliness สุดท้ายคือทุกอย่างจะต้องมีความสอดคล้องกับ Business Objective ทุกอย่างไม่ควรมากไป หรือน้อยไป ทั้งนี้เพื่อผลลัพธ์ และงบประมาณที่เหมาะสม
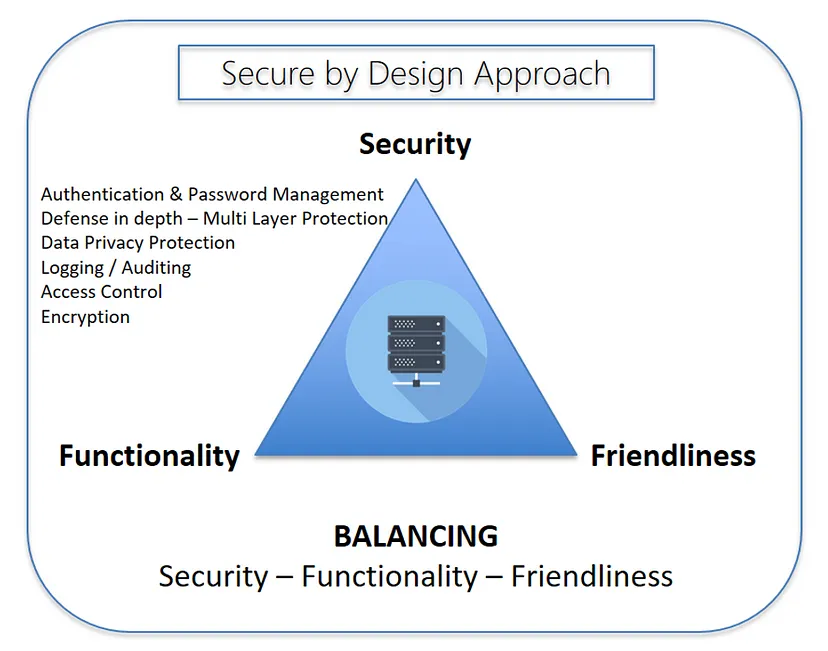
Secure by Design เป็นอีกแนวทางหนึ่งที่น่าสนใจ และให้ผลลัพธ์เป็นที่น่าพอใจอย่างมาก แต่ในความเป็นจริงการจะทำให้เป็นไปตามหลักการของ Secure by Design นั้นไม่ใช่เรื่องง่ายๆ ดังนั้น เราอาจกำหนด target ไว้โดยเริ่มจากส่วนที่มีความ critical สูง และเป็น core business ขององค์กรก่อน แน่นอนครับหากหัวใจหลักของระบบงานปลอดภัย ส่วนอื่นๆ ที่เหลือก็สามารถดูแลได้ไม่ยากเย็นนัก แต่ให้เราคำนึงถึงสิ่งหนึ่งคือ เมื่อเกิดเหตุการณ์วิกฤติขึ้นเราไม่สามารถป้องกันความเสียหายที่จะเกิดขึ้นได้ 100% ให้คิดเสมอว่า ให้เราพยายามควบคุมความเสียหายไว้ให้อยู่ในวงจำกัด โดยมุ่งเน้นเรื่องการป้องกัน Critical Asset ก่อนเป็น priority แรกๆ
แนวทางในการตรวจหาจุดอ่อนของระบบ หรือ Application เป็นอีกแนวทางหนึ่งที่จะสามารถช่วยยกระดับความปลอดภัยให้กับองค์กรได้ ในส่วนของ Secure by Design ในส่วนนี้เราจะพูดกันในเรื่องของ Secure Coding ในกรณีที่นักพัฒนา Application ทำตามหลักของ Secure Coding ก็จะทำให้ระบบงานนั้นๆ มีความปลอดภัย แต่ในโลกความเป็นจริงไม่ง่ายอย่างที่คิด มีปัจจัยหลายๆ อย่างที่ไม่สามารถทำให้เกิดผลลัพธ์ในอุดมคติได้ จากที่กล่าวมาในข้างต้นภัยคุกคามเกิดใหม่ทุกวันทำให้เราไม่สามารถบอกได้ว่าในวันข้างหน้า Application ขององค์กรจะยังคงมีความปลอดภัยอยู่ ปัจจัยไม่ได้มาจากการ coding เพียงอย่างเดียว ทั้ง OS ที่ใช้ Service ต่างๆ ที่ทำงานร่วมกับ Application ล้วนเป็นปัจจัยเสี่ยง
แนวทางป้องกัน
เมื่อเรามีการสร้าง Application ขึ้นมาใช้งานเราจะต้องดูแลรักษาไปตลอด Life-cycle หมายความว่าดูแลไปจนกว่าจะเลิกใช้ การตรวจสอบสุขภาพของ Application นั้นจะใช้หลักการตรวจหาจุดอ่อน และทดลองเจาะระบบผ่านทางจุดอ่อนที่พบเพื่อให้ทราบว่าจุดอ่อน หรือ Vulnerability ที่พบสามารถสร้างความเสียหายกับระบบได้หรือไม่ วิธีการนี้เราเรียกว่า Vulnerability Assessment และ Penetration Testing ซึ่งเป็นวิธีการที่จะช่วยในการประเมินความเสี่ยงจากจุดอ่อนที่ตรวจพบ เพื่อหาแนวทางในการปรับปรุ่งแก้ไข
ตามหลักการแล้วกระบวนการในการทำ VAPT (Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing) แต่ละครั้งจะมี 2 stage คือ Pre-Test และ Post-Test โดยทั้งสองครั้งจะมี Criteria ในการทดสอบเหมือนกันเพื่อให้สามารถตรวจวัดผลได้ถูกต้อง หลังจาก Pre-Test ทางทีมผู้ตรวจสอบจะออกรายงานแจ้งถึงผลการตรวจสอบที่พบ พร้อม Remediation Plan สำหรับการแก้ไขแต่ละส่วน หลังจากนี้จะทิ้งเวลาไว้ช่วยหนึ่งเพื่อให้เจ้าของ Application ทำการแก้ไขจุดอ่อนที่พบ หลังจากนั้นจะเข้าสู่กระบวนการ Post-Test เพื่อติดตามผล
ในการทำ Penetration Testing นี้ค่อนข้างได้รับความนิยมในปัจจุบัน โดยจะมีทั้งการซื้อเครื่องมือมาทำการทดสอบเอง หรือ บางบางองค์กรที่ติดขัดเรื่องของบุคลากร ก็อาจทำการว่าจ้างทีมงาน Tester เข้ามาช่วยในส่วนนี้ ซึ่งโดยปกติจะมีการทำ VAPT ปีละ 1–2 ครั้ง ทั้งนี้ขึ้นอยู่กับกฏข้อบังคับ หรือกฏหมายที่แต่ละองค์กรต้องปฏิบัติตาม
นอกจากจะแก้ไข หรือ Fix ที่ตัว Application แล้วนั้น องค์กรยังสามารถใช้ Security Control เข้ามาช่วยในการป้องกันได้ อาทิเช่น Host Based IPS, Web Application Firewall เป็นต้น แนวทางนี้จะสอดคล้องกับหลักการของ Defense in Depth จะช่วยในการ Delay Attack เพื่อให้ผู้ดูแลระบบมีเวลามากพอที่จะทำการแก้ไขหาทางรับมือได้ทัน แต่ทั้งนี้ก็ควรทำการ Fix ที่ตัว Application ในส่วนของ Source Code, Patch OS จะเป็นการปิดช่องโหว่ได้ดีที่สุด